Simple Present
The Present Simple is the most basic tense in the English language. It is an interesting tense because it can be used to express the future. Generally, though, we use it to describe the present activities or to talk about routines or habits.
Basic form
Subject + Verb (present form)
Quick examples
- John lives in New York.
- We play football every day.
- You are really kind.
- The meeting starts at 3 PM.
Use
- Facts, generalizations and universal truths
- Habits and routines
- Permanent situations
- Events that are certain to happen
- Arrangements that we can't change (e.g. timetables, official meetings)
- State verbs (e.g. be, have, suppose, know)
- Narrations, instructions or commentaries
To understand this use better, watch this interactive animation:
[ Scientist: The Earth goes around the Sun ]
Explanation
In this cartoon, you can see a scientist who says: "The Earth goes around the Sun".
- Why is the Present Simple used in this sentence? Because the scientist expresses a fact, something that he believes is true (in this case, he is right: the Earth really orbits the Sun).
Use 2: Habits and Routines
We also use this tense to describe actions that happen frequently. For example: habits, routines, tendencies.
- We leave for work at 7:30 AM every morning. Routine
- My husband watches the TV in the evening. Habit, Routine
- Susan often meets with her friends after school. Habit, Routine
- They usually play football on Sunday. Habit, Routine
- Mark rarely visits his sick grandmother. Tendency
- Pinocchio usually tells lies. Tendency
Adverbs of Frequency
The Present Simple is often used with the frequency adverbs:
- always
- frequently/often
- usually
- seldom/rarely
- nowadays
- never
- every week/year
- sometimes/occasionally
- from time to time
- every now and then
A few examples how to use them in sentences:
- I always go to church on Sundays.
- I never eat anything after 10 PM.
To understand this use better, watch this interactive animation:
[ John: I play basketball every Friday ]
Use 3: Pernament Situations
Use the Present Simple to talk about situations in life that last a relatively long time.
- I live in Boston
- He works as a fireman.
- Margaret drives a Volkswagen.
- Jerry doesn't teach maths at highschool.
Use 4: Events Certain to Happen
Use the Present Simple when an event is certain to happen in the future.
- My grandmother turns 100 this July.
- Winter starts on December 21.
Use 5: State Verbs
You should use the Present Simple with state verbs.
- I like swimming.
- We know this man.
Speaker 1: Ronaldinho, do you like
football?
Ronaldinho: Yes, I do.
Note
Some of the verbs used in the simple form can also appear in the continuous form. This is typically when they have an active meaning or emphasize change.
- I'm thinking of moving to San Francisco.
- I'm loving your new hairdo!
Use 6: Future Arrangements
Use the Present Simple to talk about events that we can't change (for example, an official meeting or a train departure).
- The meeting starts at 4 PM.
- The train leaves at the noon.
- When does the plane take off?
- Jerry doesn't teach maths at high school.
Use 7: Narrations, Instructions or commentaries
The Present Simple is also used in narrations (e.g. to tell a story or a joke), instructions (e.g. cooking) or commentaries (especially sport commentaries).
- "A man goes to visit a friend and is amazed to find him playing chess with his dog. He watches the game in astonishment for a while [...]"
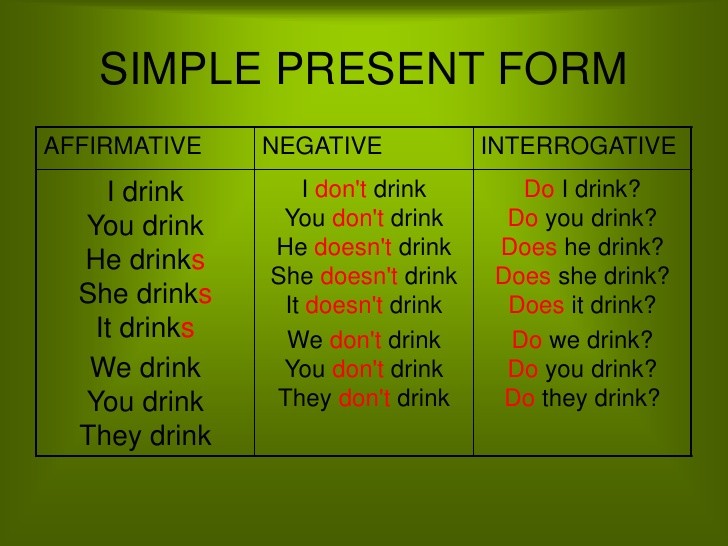
Form
Forming a sentence in the Present Simple is easy. To form a declarative sentence, all you need is the subject of the sentence (e.g. I, you, he, a dog) and the verb (e.g. be, talk, swim). Questions and negative sentences are only a little more difficult, because they require an auxiliary verb.
Declarative Sentences
|
Subject |
+ |
Verb (present form) |
|
e.g. he, she, a dog, etc. |
e.g. go, make, have, etc. |
Sharks have sharp teeth (Use 1)
|
Examples |
|
A dog is an animal. |
|
I learn English twice a week. |
|
I have two eggs. |
|
The course starts in April. |
|
The man enters the room and looks at the clock. |
Questions Simple Present
Questions require the auxiliary verb "to do" or, in the third person singular, "does".
|
Do or Does |
+ |
Subject |
+ |
Verb (present form) |
|
e.g. he, she, a dog, etc. |
e.g. go, make, have, etc. |
Compare these examples:
- Person A: Does she like going to the mountains?
- Person B: Yes, she does.
- Person A: Does John have a dog?
- Person B: No, he doesn't.
When asking a question, the verb does not conjugate:
- Does she have a dog?
-
Does she has a dog?
For the verb "to be", we do not use an auxiliary:
- Is he tall?
-
Does he be tall?
|
Examples |
|
Is he a lawyer? |
|
Does Mike go swimming every Sunday? |
|
Does she live in London? |
|
Do you turn 40 in April? |
Negative Sentences
|
Subject |
+ |
Don't or Doesn't |
+ |
Verb (present form) |
|
e.g. he, she, a dog, etc. |
e.g. go, make, have, etc. |
Contracted forms
- do + not = don't
- does + not = doesn't
|
Examples |
|
They don't live in New York anymore. |
|
I don't like winter. |
|
He doesn't go to the cinema at all. |
|
Spring doesn't start in December. |
EXERCISE

VERBS
